Use of Complimentary Alternative Medicine (CAM) is widespread. The 2007 National Health Interview Survey, a nationwide Government survey, found that 38 percent of U.S. adults reported using CAM in the previous 12 months, with the highest rates among people aged 50–59 (44 percent)1. The NHIS data also revealed that approximately 42 percent of adults who used CAM in the past 12 months disclosed their use of CAM to a physician (M.D.) or osteopathic physician (D.O.)2. Because many adults also use over-the-counter medications, prescription drugs, or other conventional medical approaches to manage their health, communication between patients and health care providers about CAM and conventional therapies is vital to ensuring safe, integrated use of all health care approaches.
CAM is defined as a group of diverse medical and health care systems, practices, and products that are not generally considered part of conventional medicine. CAM includes such products and practices as herbal or dietary supplements, meditation, chiropractic care, and acupuncture.
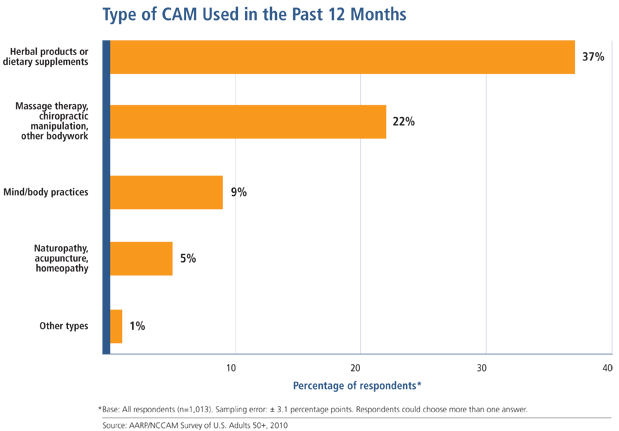
In the 2010 AARP/NCCAM survey, just over half (53 percent) of people 50 and older reported using CAM at some point in their lives, and nearly as many (47 percent) reported using it in the past 12 months. Herbal products or dietary supplements were the type of CAM most commonly used, with just over a third (37 percent) of respondents reporting their use, followed by massage therapy, chiropractic manipulation, and other bodywork, used by around a fifth (22 percent) of respondents (see above figure).